This article is written by Akshita Sodhi,
Fourth year law student
lloyd law college.
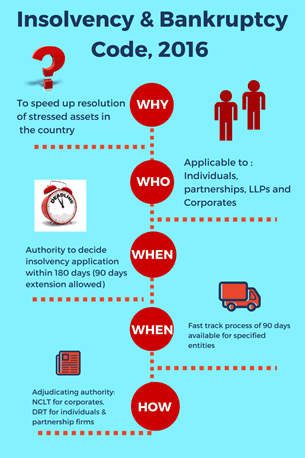
The code of Insolvency and bankruptcy was passed in the year 2016. This code was enacted with the purpose to provide fast relief to creditors in case their debtors become insolvent. This code provides a time bound process to provide the relief to the debtors.
It must be noted that recently in the wake of COVID- 19, a new section(section 10 A) in IBC 2016 a new section is inserted for the suspension of initiation of insolvency proceedings against the corporate debtor. But this provision shall be applicable for any default arising after 25th march 2020 up to the period of six months.
What is Insolvency?
Insolvency is a state of financial and economic distress where the debtor becomes insolvent, i.e., he becomes unable to pay his debts to the creditor. Under IBC Code, 2016, Corporate Insolvency and bankruptcy proceedings can be initiated by the creditor. against a debtor on the minimum amount of default of Rs 1 lakh.
What is bankruptcy?
Bankruptcy is the order given by the court for the debtor where the court initiates legal proceedings for the debtor to repay his debts.
What is liquidation?
The liquidation is the process of selling goods and assets of the bankrupt person or entity to let the debtor to repay his debt.
Applicability of the act.
This act is applicable to all the companies incorporated under Companies Act, 2013, or the company incorporated under any act applicable during the due course of time, limited liability partnerships incorporated under limited liability partnership act, 2013, partnerships firms and individuals or any such other body incorporated under any act or law for the time being in force.
Who can file an application under the act?
Corporate insolvency resolution proceedings can be initiated by a financial creditor, operational creditor or by the corporate debtor itself.[1]
Corporate person
Co-operate person includes company registered under the companies act 2013, Limited Liability Partnership (llp), a partnership firm, or any other person incorporated with limited liability under any law at the time being in force except financial service providers.[2]
Adjudicating authority under the Code
NCLT(National Company Law Tribunal), DRT(Debt recovery tribunal). NCLT is the adjudicating authority for corporate debtors and personal guarantees. DRT is the adjudicating authority for individuals and partnership firms.
Appellate Court
If someone is satisfied by the order of NCLT, an application can also be filled in NCLAT within 30 days of receipt of such order. If the debtor is not satisfied by the order of NCLAT, he can file an application in the supreme court within 45 days of such order.
Creditor
Creditor is the one who credits money/goods to the debtor. In other words, Creditor is the one to whom any person/ entity/ company owes money.
Debtor
Debtor is the person who owes the debt. In short, the debtor is the one to whom the creditor gives money.
Debt
Debt is the obligation to pay or repay the money to the one who lends you the same.
Financial creditor
In order to understand financial creditors, it is crucial to first know what is ‘financial debt’.
Financial creditor is the one to whom a financial debt is owed and includes a person to whom such debt has been legally assigned or transferred.[3]. The relation between the financial creditor and debtor is purely of cash. Example- loan given by bank, the person who give loan on interest etc.
Operational creditor
In order to understand the concept of operational debtor, it is important to know the meaning of operational debt, ‘operational debt’ means a claim in respect of the provisions of goods or services including employment or a debt in respect of the repayment of the dues arising under any law for the time being in force and payable to the Central Government, any State Government or any local authority.[4].
In short, an operational creditor is the one who has any amount due towards the debtor and the amount is due because of supply of goods, services including government dues, taxes etc. Examples of operational creditors are employers of the company, service providers of a company etc.
In a recent judgement, the Supreme Court has cleared that, operational debt is only confined to goods, services, government and employees dues and home buyers don’t fall in the ambit of this definition.
IRP
insolvency resolution professional appointed by the court for resolving the co-operate insolvency resolution process initiated against the debtor.
Time Period for completing insolvency proceedings
180 days( 90 days-extended period can also be given on the discretion of the court. )
PROCESS INVOLVED UNDER INSOLVENCY AND BANKRUPTCY CODE 2016
| Sending of demand notice to the defaulter giving him a 10 day notice period to clear his dues. |
| Initiation of corporate insolvency resolution process, i.e. filing of application against the debtor if he doesn’t clear dues within 10 days of receipt of the demand notice or brings it notice to the creditor about the existence of any previous suit or arbitration proceedings filed or pending before the sending of notice. |
| Within 14 days of the receipt of the application, the court can either accept it if it is complete or reject it if it is incomplete. |
| Appointment of Insolvency resolution professional by the court as proposed by the creditor. |
| After the appointment of interim resolution professionals by the court, all the rights of the directors, partners etc shall be vested in the hand of appointed interim resolution professionals. Moreover all the affairs of the debtor shall be managed by the interim resolution professionals. Appointed managers or auditors or any other financial institutions shall report to the appointed interim resolution professionals and provide all the details if so needed by him or he asks them for the same. |
| All the acts/deeds of the debtor shall be executed in the name of the appointed interim resolution professional. Moreover he should also have control over the financial information including balance sheet, ledger or any other document specified. |
| All the information relating to assets, property of the bankrupt debtor is being collected by the interim resolution professional. He shall also receive and pursuant claims made by the other creditors as well pending against the bankrupt debtor. |
| Formation of committee of creditors by the interim resolution professional. |
| Within 7 days of the formation of the committee of creditors, the first meeting shall be held and the members of the committee of creditors will decide whether they want the appointed interim resolution professional to be resolutional professional for further proceedings or whether they want to appoint new resolutional professional for further proceedings by 75% majority. The decision of the committee shall be informed to the adjudicating authority and the interim resolution professional as well. |
| Formation of resolution plan by the resolutional applicant and submission of the same to the resolutional professional. |
| The resolutional professional will check the resolution plan and the same is also being submitted to the committee of creditors and should also be approved by the committee of creditors by more than 75% voting. |
| The resolution plan is then submitted to the court. |
| If the court approves the resolution plan, the order by the court shall be binding on corporate debtors and all its employees as well. |
| The corporate debtor can also make an appeal to the appellate court if he is not satisfied by the decision of the court. |
| The court can even order for the liquidation process for the co-operate as it deems fit or if the same is being requested by the resolutional professional( in discussion and voting with committee of creditors) before the submission of resolution plan. |
| The liquidation process is initiated by the court in the same easy, the resolution process is initiated. |
Endnotes:-
[1]-Section 6 of IBC code 2016.
[2]- Section 3(7) of IBC code 2016
[3]-Section 5(7) of IBC code 2016.
[4]-Section 5(21) of IBC code 2016.